Theory Of Production
This document was uploaded by user and they confirmed that they have the permission to share it. If you are author or own the copyright of this book, please report to us by using this DMCA report form. Report DMCA
Overview
Download & View Theory Of Production as PDF for free.
More details
- Words: 562
- Pages: 3
Theory of Production Production: Basic concept • Transformation of input into output • Creation of utility • Act of creation of utility by transforming the Input (land, labor, capital and raw material) into output through organizing and combining the productive resources Production is related to: – Physical change of the objects, and – Services that satisfies the intangible needs of human being. • Therefore the scope of the term production covers the manufacturing activities like Rice, cloth and cars as well as the services like banking, transportation, media etc..
Production function • Relationship between maximum amount of output that can be produced and the inputs required to produce that output • It is defined for a given level of technology and therefore there can be a number of production function for each product under different state of technology
Factors of production • Hundreds and thousands of factors can be used • They can be classified under 4 broad generic factors – Land – Labor – Capital – Entrepreneurship
Factors of production - Land • It means all the natural resources, which yields income or which has exchange value • In the other word, it refers to all the natural resources, which is used in production. Land – Features • Land is free gift of nature • It has fixed quantity of supply • It is permanent in nature • Lack of geographical mobility • Infinite variety
Labor • Any “Human Effort” involved in the production function in exchange of money. • Unlike the ordinary use which means only the physical and unskilled work, labor, in economics means manual or physical work which is undertaken for monetary consideration. Labor- Features • Inseparable from laborer • Has to be sold in person • Doesn’t last long • Late adjustment in supply as a result of change in price
Capital • Produced means of production • It is that part of the produced elements that is further used in production instead of being consumed directly Capital – features • Capital is produced element • Capital has certain longevity • It is mobile • Amount capital can be increased through human effort • Income from capital is uniformed if it is used with same degree of efficiency
Organization/ Entrepreneurship • Human element that initiates and directs the production process by combining the productive resources • Differs from labors in the following ways: • Labor responsible for a particular job, where as entrepreneur responsible for whole production process • Labor’s return is fixed and assured where as case is opposite for entrepreneur’s return Entrepreneurship – features • Decision Maker • Brings the productive resources together • Risk taker • Innovator
Marginal, Average and Total Production Three important production concepts stating the relationship of a single input with the output • Marginal Product Marginal Product of an input is the extra amount of product that has been produced by applying 1 unit of that input holding other factors constant. It measures the additional units of output that can be obtained by using extra unit of an input after certain limit. • Average product Average output produced by one unit of input at a certain level of input being used. calculated by diving the total output by the number of the input being used. • Total product It is the total volume of out put at a given time
Production function • Relationship between maximum amount of output that can be produced and the inputs required to produce that output • It is defined for a given level of technology and therefore there can be a number of production function for each product under different state of technology
Factors of production • Hundreds and thousands of factors can be used • They can be classified under 4 broad generic factors – Land – Labor – Capital – Entrepreneurship
Factors of production - Land • It means all the natural resources, which yields income or which has exchange value • In the other word, it refers to all the natural resources, which is used in production. Land – Features • Land is free gift of nature • It has fixed quantity of supply • It is permanent in nature • Lack of geographical mobility • Infinite variety
Labor • Any “Human Effort” involved in the production function in exchange of money. • Unlike the ordinary use which means only the physical and unskilled work, labor, in economics means manual or physical work which is undertaken for monetary consideration. Labor- Features • Inseparable from laborer • Has to be sold in person • Doesn’t last long • Late adjustment in supply as a result of change in price
Capital • Produced means of production • It is that part of the produced elements that is further used in production instead of being consumed directly Capital – features • Capital is produced element • Capital has certain longevity • It is mobile • Amount capital can be increased through human effort • Income from capital is uniformed if it is used with same degree of efficiency
Organization/ Entrepreneurship • Human element that initiates and directs the production process by combining the productive resources • Differs from labors in the following ways: • Labor responsible for a particular job, where as entrepreneur responsible for whole production process • Labor’s return is fixed and assured where as case is opposite for entrepreneur’s return Entrepreneurship – features • Decision Maker • Brings the productive resources together • Risk taker • Innovator
Marginal, Average and Total Production Three important production concepts stating the relationship of a single input with the output • Marginal Product Marginal Product of an input is the extra amount of product that has been produced by applying 1 unit of that input holding other factors constant. It measures the additional units of output that can be obtained by using extra unit of an input after certain limit. • Average product Average output produced by one unit of input at a certain level of input being used. calculated by diving the total output by the number of the input being used. • Total product It is the total volume of out put at a given time
Related Documents

Theory Of Production
April 2020 12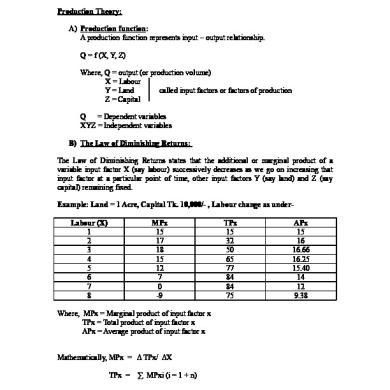
Production Theory
May 2020 21
Production Theory And Estimation
June 2020 17
Fourth Lecture - Theory Of Production-2
June 2020 3
