Islamic Banking-basic Principles
This document was uploaded by user and they confirmed that they have the permission to share it. If you are author or own the copyright of this book, please report to us by using this DMCA report form. Report DMCA
Overview
Download & View Islamic Banking-basic Principles as PDF for free.
More details
- Words: 697
- Pages: 8
Basic Principles of Islamic Banking: An Overview Prof Abdullah Saeed University of Melbourne [email protected]
The presentation will cover • • • •
Historical overview Basic framework and key concepts Permissible and prohibited contracts Application of key concepts to banking
1
Historical Overview • Dealing with money, investment on profit and loss sharing • Attitude to interest: Sharia on the whole did not accept the legitimacy of interest • Western banks in Muslim countries: interest • Literature on banking without interest: 20th century • Practical steps: village banks in Egypt • Islamic Development Bank in Jeddah • Islamic commercial banks • Today: network of Islamic banks with a range of products competing with interest-based banks
Basic Framework-1: Wealth and Ownership • Wealth as trust – Right of the needy; circulation; spending; hoarding
• Ownership – Trust; individual/community rights; – Ways and means: • labour; gift; inheritance • all ways and means to acquisition must be halal • Object of ownership: must be halal
2
Basic Framework Concept of Halal and Haram - 1 • Basic principle: – Generally all ways and means are halal (except those that are clearly prohibited). – Prohibition is always an exception
Basic Framework: Concept of Halal and Haram - 2 • Some of the haram ways and means of acquiring wealth: – – – – – – – –
through riba (interpreted as ‘interest’) cheating and fraud: quality, measure, weight games of chance (lotteries, betting) creating artificial scarcities manipulation of prices sale and dealing in haram products engaging in haram professions (eg prostitution) exploitation of the poor, the needy and disadvantaged
3
Basic Framework: Concept of Money • Money as a form of wealth • Money: – primary function: medium of exchange – No price should be charged for money – Basic rule in lending: return an equal amount
Basic Framework: Prohibition of Riba • • • •
Riba as interest (differences among Muslims) Interest in all forms prohibited All interest-based transactions should be avoided Interest-based transactions are seen as ‘unjust’: risk on the borrower
4
Contracts in Islamic Finance Permissible and Prohibited Contracts • Contracts: – in transactions should be permissible (re Sharia) – should be based on mutual agreement – should not be based on: riba, haram, fraud etc
• Terms that both parties agree to (and are not based on haram) are acceptable
Banks • Important institutions but should not be based on interest • Banks should be in line with the requirements of Islamic law • Alternative ways of operating banks and financial institutions should be found
5
Interest-based system, risk and profit • Problems with the system: – risk on the borrower
• • • •
Profit related to risk Risk should be shared: both parties Profit should be shared on an agreed upon ratio Loss should be shared strictly according to capital contribution
Banks: Profit and Loss Sharing (PLS) • Banking business should be based on PLS: – the deposits & investments – PLS contracts of mudaraba and musharaka will form the backbone of Islamic banking
• PLS contracts of mudaraba and musharaka will form the backbone of Islamic banking • Both contracts are developed in Islamic law Important to refer to Islamic legal texts to understand the nature of these contracts
6
PLS and Deposits • • • •
Bank will mobilise deposits on the basis of PLS PLS contract of mudaraba is used Features of mudaraba contract (bank:depositors) Relationship of the Bank with the Depositors
PLS and Investments • PLS contracts of mudaraba and musharaka should be used • Other forms of non-PLS contracts are also used (murabaha) • Fee-based services can be provided • Relationship of the Bank with its investment clients (mudaraba, musharaka, murabaha)
7
Objectives of Islamic Banks: An Example • To help Muslims, execute their financial dealings in strict respect of the ethical, individual and social values of the Shariah, without contravening the prohibition of dealing in riba (interest or usury). • To Serve all Muslim communities in mobilising and utilising the financial resources needed for their economic development and prosperity. • To serve the Islamic communities and other nations by strengthening the economic and financial cooperation for economic development
8
The presentation will cover • • • •
Historical overview Basic framework and key concepts Permissible and prohibited contracts Application of key concepts to banking
1
Historical Overview • Dealing with money, investment on profit and loss sharing • Attitude to interest: Sharia on the whole did not accept the legitimacy of interest • Western banks in Muslim countries: interest • Literature on banking without interest: 20th century • Practical steps: village banks in Egypt • Islamic Development Bank in Jeddah • Islamic commercial banks • Today: network of Islamic banks with a range of products competing with interest-based banks
Basic Framework-1: Wealth and Ownership • Wealth as trust – Right of the needy; circulation; spending; hoarding
• Ownership – Trust; individual/community rights; – Ways and means: • labour; gift; inheritance • all ways and means to acquisition must be halal • Object of ownership: must be halal
2
Basic Framework Concept of Halal and Haram - 1 • Basic principle: – Generally all ways and means are halal (except those that are clearly prohibited). – Prohibition is always an exception
Basic Framework: Concept of Halal and Haram - 2 • Some of the haram ways and means of acquiring wealth: – – – – – – – –
through riba (interpreted as ‘interest’) cheating and fraud: quality, measure, weight games of chance (lotteries, betting) creating artificial scarcities manipulation of prices sale and dealing in haram products engaging in haram professions (eg prostitution) exploitation of the poor, the needy and disadvantaged
3
Basic Framework: Concept of Money • Money as a form of wealth • Money: – primary function: medium of exchange – No price should be charged for money – Basic rule in lending: return an equal amount
Basic Framework: Prohibition of Riba • • • •
Riba as interest (differences among Muslims) Interest in all forms prohibited All interest-based transactions should be avoided Interest-based transactions are seen as ‘unjust’: risk on the borrower
4
Contracts in Islamic Finance Permissible and Prohibited Contracts • Contracts: – in transactions should be permissible (re Sharia) – should be based on mutual agreement – should not be based on: riba, haram, fraud etc
• Terms that both parties agree to (and are not based on haram) are acceptable
Banks • Important institutions but should not be based on interest • Banks should be in line with the requirements of Islamic law • Alternative ways of operating banks and financial institutions should be found
5
Interest-based system, risk and profit • Problems with the system: – risk on the borrower
• • • •
Profit related to risk Risk should be shared: both parties Profit should be shared on an agreed upon ratio Loss should be shared strictly according to capital contribution
Banks: Profit and Loss Sharing (PLS) • Banking business should be based on PLS: – the deposits & investments – PLS contracts of mudaraba and musharaka will form the backbone of Islamic banking
• PLS contracts of mudaraba and musharaka will form the backbone of Islamic banking • Both contracts are developed in Islamic law Important to refer to Islamic legal texts to understand the nature of these contracts
6
PLS and Deposits • • • •
Bank will mobilise deposits on the basis of PLS PLS contract of mudaraba is used Features of mudaraba contract (bank:depositors) Relationship of the Bank with the Depositors
PLS and Investments • PLS contracts of mudaraba and musharaka should be used • Other forms of non-PLS contracts are also used (murabaha) • Fee-based services can be provided • Relationship of the Bank with its investment clients (mudaraba, musharaka, murabaha)
7
Objectives of Islamic Banks: An Example • To help Muslims, execute their financial dealings in strict respect of the ethical, individual and social values of the Shariah, without contravening the prohibition of dealing in riba (interest or usury). • To Serve all Muslim communities in mobilising and utilising the financial resources needed for their economic development and prosperity. • To serve the Islamic communities and other nations by strengthening the economic and financial cooperation for economic development
8
Related Documents

Islamic Planning Principles
May 2020 4
Principles Of Islamic Faith
April 2020 10
Principles Of Islamic Banking
June 2020 12
Islamic Banking-basic Principles
May 2020 27
Islamic Finance Principles
May 2020 9
Principles Of Islamic Political System
April 2020 8More Documents from ""
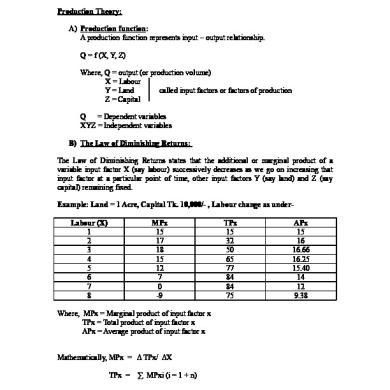
Production Theory
May 2020 21
Islami Song
June 2020 20
Bill Of Lading
July 2020 19
Incentives For Exporters
July 2020 27
Managing Marteing Channels
May 2020 0