Pricing & Costing:: Including Budgeting & Life Cycle Costing
This document was uploaded by user and they confirmed that they have the permission to share it. If you are author or own the copyright of this book, please report to us by using this DMCA report form. Report DMCA
Overview
Download & View Pricing & Costing:: Including Budgeting & Life Cycle Costing as PDF for free.
More details
- Words: 1,495
- Pages: 45
Pricing & Costing: including budgeting & life cycle costing Anjana Vivek [email protected] www.bizkul.com
1
Costs: Some terms
Direct Indirect Committed Flexible
www.bizkul.com
2
Costs
Fixed Variable Semi variable
www.bizkul.com
3
Exercise Revenue- Restaurant Restaurant Direct - Restaurant Restaurant Indirect - Restaurant Restaurant
A B A B A B
– – – – – –
Rs. 10,00,000 Rs. 4,00,000 Rs. 6,00,000 Rs. 2,20,000 Rs. 2,00,000 Rs. 80,000
What is the profit margin ?? www.bizkul.com
4
Exercise Revenue- Restaurant Restaurant Direct - Restaurant Restaurant Indirect - Restaurant Restaurant
A B A B A B
– – – – – –
Rs. 10,00,000 Rs. 4,00,000 Rs. 6,00,000 Rs. 2,20,000 Rs. 2,00,000 Rs. 80,000
What are your thoughts on the profit so calculated? www.bizkul.com
5
Exercise Revenue- Restaurant Restaurant Direct - Restaurant Restaurant Indirect - Restaurant Restaurant
A B A B A B
– – – – – –
Rs. 10,00,000 Rs. 4,00,000 Rs. 6,00,000 Rs. 2,20,000 Rs. 2,00,000 Rs. 80,000
Do you think this is the true profit? How has indirect cost been calculated (allocated)? What are your views on the costing? www.bizkul.com
6
Exercise Revenue- Restaurant Restaurant Direct - Restaurant Restaurant Indirect - Restaurant Restaurant
A B A B A B
– – – – – –
Rs. 10,00,000 Rs. 4,00,000 Rs. 6,00,000 Rs. 2,20,000 Rs. 2,00,000 Rs. 80,000
How does change in basis of allocation impact profit ? www.bizkul.com
7
Solution Case I Amt Rs. Restaurant Revenues
A
B
Total
1,000,000
400,000
1,400,000
Direct
600,000
220,000
820,000
Indirect
200,000
100,000
300,000
Margin
200,000
80,000
280,000
20
20
20
% margin
www.bizkul.com
8
Alternate scenario Case II Amt Rs. Restaurant Revenues
A
B
Total
1,000,000
400,000
1,400,000
Direct
600,000
220,000
820,000
Indirect
150,000
150,000
300,000
Margin
250,000
30,000
280,000
25
7.5
20
% margin
www.bizkul.com
9
Costs
Costs are incurred in a variety of functions in business – Establishing business – R&D – Production / Delivery of service – Sales and marketing – After sales service – Administration www.bizkul.com
10
Importance of costing
Planning Controlling Decision making Implementing Continuous improvement www.bizkul.com
11
Costs
Controllable Joint Discretionary Relevant Sunk Opportunity www.bizkul.com
12
Costs: Analysis
Useful to decide what is controllable and what is not Helps to understand what is relevant to decision making Must be done with care to avoid incorrect decisions
www.bizkul.com
13
Relevant costs
Expected future costs to help in making decisions Differ with alternate courses of action – Managers make decisions based on costs allocated – Managers may make short run decisions that may affect long term business and sales
Relevant costs help choose between alternatives www.bizkul.com
14
Costs - relevant / not relevant
Equipment replacement – Book value of old equipment – not relevant – Current disposal price of old equipment – relevant – Cost of equipment - relevant
www.bizkul.com
15
Costing: Some terms
Contribution margin Break even point
www.bizkul.com
16
Break even point
Ram Kumar wants to sell Computer tables and chairs at a conference stall He estimates that he can sell each unit for Rs. 10,000 each The cost per unit is Rs. 6,000 The stall rent is Rs. One lakh How many units must Ram Kumar sell to break even? www.bizkul.com
17
Break even point
In continuation of the previous example, assume that Rs.6000 is not cost, ie assume some raw material which is anyway spare – eg. wood, is used for this purpose. So this cost actually may not be relevant, thou labour cost may be relevant then what happens to your decision? Try to develop a different perspective and way of thinking www.bizkul.com
18
Costing: Some terms Contribution margin = Sales – total variable cost
www.bizkul.com
19
Costs: Analysis
Identify cost objects / cost centres Accumulate costs Assign / trace costs to cost objects
www.bizkul.com
20
Assignment / Allocation Selection of Activity base – people; machine hours; material consumed Activity level – normal/abnormal
www.bizkul.com
21
Budgets
Plan performance in advance for a given time frame Review performance with budget Understand reasons for variation Take remedial measures if required Plan again based on actual performance and feedback www.bizkul.com
22
Budgets
Keep company objectives in mind Long term and short term Rolling budgets
www.bizkul.com
23
Budgets
Master budget, comprising of detailed budgets for eg. budgets for – Income – Production – Direct costs – R&D – Administration www.bizkul.com
24
Product budget
Expected sale Inventory on hand Production schedule Direct costs Indirect costs Company policies and strategy www.bizkul.com
25
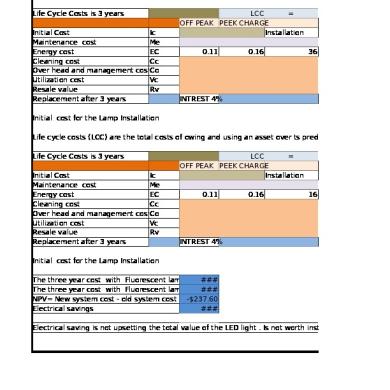
Life cycle costing
Considers entire life cycle of product from start to finish Provides important information for pricing decisions For example, if a mobile phone is built, if the R&D costs are high for the company, the repairs and maintenance cost to the customer may be low; so the life cycle is across the life of the product and considers costs www.bizkul.com and impact on prices 26
Life cycle costs
Upstream costs – R&D, design, prototyping, testing, quality development
Manufacturing/Operations costs – Purchasing, manufacture/service
Downstream costs – marketing, sales and distribution, customer service and warranty www.bizkul.com
27
Life cycle costs
Product life cycle costs vary with industry and nature of industry R&D is not only at start of product life, this may also occur at other stages, ie development of additional features in product Life cycle may also depend on markets targeted, ie country, region, socio-economic background etc. www.bizkul.com 28
Implementation of LCC
Identify stages in product life cycle Identify target customer Understand target customers perspective and estimate need Analyse cost and pricing in detail Educate employees about LCC www.bizkul.com
29
Implementation of LCC
Develop product and pricing structure based on LCC Create appropriate organisation structure for implementation Educate customer on LCC, eg. mobile phone referred to in earlier slide Focus on strategic marketing to address customer requirements and needs, stated and unstated Continuous life cycle budgeting and monitoring and modify/change as required www.bizkul.com 30
Life cycle costing benefits
Optimisation of profit over product life Full set of costs associated with products are ascertained – Most accounting systems capture manufacturing costs – Other areas like R&D at start and customer service as close do not get much importance www.bizkul.com
31
Life cycle costing benefits
Differences in percentages in committed costs at initial stage of business is highlighted – The higher the initial costs, the more critical it is for management to develop better predictions about revenues
www.bizkul.com
32
Life cycle costing benefits
Interrelationships across cost categories are highlighted – Many companies with high R&D & product refinement costs may experience less customer service costs and vice versa. Such costs are often hidden and affect quality of product
www.bizkul.com
33
Pricing
Intuitive Rule of thumb Trial and error Discount Premium Mark up www.bizkul.com
34
Pricing decisions Influenced by Costs Competitors Customers Time horizon – short run or long run decisions Strategic reasons www.bizkul.com
35
Target Pricing
Develop product Set target price Try to achieve target cost Target cost = Competitive price – desired profit www.bizkul.com
36
Pricing for short run
Decide on relevant costs that should be used Compute costs, direct, indirect and total Compute any special costs that need to be incurred and savings that may be possible Decide on pricing based on other factors such as long term impact, competition etc. www.bizkul.com
37
Pricing for long run
Important to consider long term pricing for long term sustainability and growth of business Initial pricing and short term pricing should keep long term pricing in mind Image and brand of business to be considered in pricing Costs to be understood and allocated Consistency in pricing in long term www.bizkul.com
38
…..to trigger thinking
www.bizkul.com
39
A cup of coffee
A cup of coffee costs Rs. 10 to make
HOW will you plan to price this?
……….. continued.. www.bizkul.com
40
A cup of coffee
Will you charge based on the price of coffee in similar coffee shops and restaurants?
……….. continued.. www.bizkul.com
41
A cup of coffee
Will you charge cost plus a margin?
……….. continued..
www.bizkul.com
42
A cup of coffee
OR will you think differently?
……….. continued..
www.bizkul.com
43
A cup of coffee For example …
You could charge differently during the rush hour You could have special rates in non rush hours
www.bizkul.com
44
Some thoughts… You can … if you want
Think differently about your pricing Think differently about your negotiations for pricing and selling www.bizkul.com
45
1
Costs: Some terms
Direct Indirect Committed Flexible
www.bizkul.com
2
Costs
Fixed Variable Semi variable
www.bizkul.com
3
Exercise Revenue- Restaurant Restaurant Direct - Restaurant Restaurant Indirect - Restaurant Restaurant
A B A B A B
– – – – – –
Rs. 10,00,000 Rs. 4,00,000 Rs. 6,00,000 Rs. 2,20,000 Rs. 2,00,000 Rs. 80,000
What is the profit margin ?? www.bizkul.com
4
Exercise Revenue- Restaurant Restaurant Direct - Restaurant Restaurant Indirect - Restaurant Restaurant
A B A B A B
– – – – – –
Rs. 10,00,000 Rs. 4,00,000 Rs. 6,00,000 Rs. 2,20,000 Rs. 2,00,000 Rs. 80,000
What are your thoughts on the profit so calculated? www.bizkul.com
5
Exercise Revenue- Restaurant Restaurant Direct - Restaurant Restaurant Indirect - Restaurant Restaurant
A B A B A B
– – – – – –
Rs. 10,00,000 Rs. 4,00,000 Rs. 6,00,000 Rs. 2,20,000 Rs. 2,00,000 Rs. 80,000
Do you think this is the true profit? How has indirect cost been calculated (allocated)? What are your views on the costing? www.bizkul.com
6
Exercise Revenue- Restaurant Restaurant Direct - Restaurant Restaurant Indirect - Restaurant Restaurant
A B A B A B
– – – – – –
Rs. 10,00,000 Rs. 4,00,000 Rs. 6,00,000 Rs. 2,20,000 Rs. 2,00,000 Rs. 80,000
How does change in basis of allocation impact profit ? www.bizkul.com
7
Solution Case I Amt Rs. Restaurant Revenues
A
B
Total
1,000,000
400,000
1,400,000
Direct
600,000
220,000
820,000
Indirect
200,000
100,000
300,000
Margin
200,000
80,000
280,000
20
20
20
% margin
www.bizkul.com
8
Alternate scenario Case II Amt Rs. Restaurant Revenues
A
B
Total
1,000,000
400,000
1,400,000
Direct
600,000
220,000
820,000
Indirect
150,000
150,000
300,000
Margin
250,000
30,000
280,000
25
7.5
20
% margin
www.bizkul.com
9
Costs
Costs are incurred in a variety of functions in business – Establishing business – R&D – Production / Delivery of service – Sales and marketing – After sales service – Administration www.bizkul.com
10
Importance of costing
Planning Controlling Decision making Implementing Continuous improvement www.bizkul.com
11
Costs
Controllable Joint Discretionary Relevant Sunk Opportunity www.bizkul.com
12
Costs: Analysis
Useful to decide what is controllable and what is not Helps to understand what is relevant to decision making Must be done with care to avoid incorrect decisions
www.bizkul.com
13
Relevant costs
Expected future costs to help in making decisions Differ with alternate courses of action – Managers make decisions based on costs allocated – Managers may make short run decisions that may affect long term business and sales
Relevant costs help choose between alternatives www.bizkul.com
14
Costs - relevant / not relevant
Equipment replacement – Book value of old equipment – not relevant – Current disposal price of old equipment – relevant – Cost of equipment - relevant
www.bizkul.com
15
Costing: Some terms
Contribution margin Break even point
www.bizkul.com
16
Break even point
Ram Kumar wants to sell Computer tables and chairs at a conference stall He estimates that he can sell each unit for Rs. 10,000 each The cost per unit is Rs. 6,000 The stall rent is Rs. One lakh How many units must Ram Kumar sell to break even? www.bizkul.com
17
Break even point
In continuation of the previous example, assume that Rs.6000 is not cost, ie assume some raw material which is anyway spare – eg. wood, is used for this purpose. So this cost actually may not be relevant, thou labour cost may be relevant then what happens to your decision? Try to develop a different perspective and way of thinking www.bizkul.com
18
Costing: Some terms Contribution margin = Sales – total variable cost
www.bizkul.com
19
Costs: Analysis
Identify cost objects / cost centres Accumulate costs Assign / trace costs to cost objects
www.bizkul.com
20
Assignment / Allocation Selection of Activity base – people; machine hours; material consumed Activity level – normal/abnormal
www.bizkul.com
21
Budgets
Plan performance in advance for a given time frame Review performance with budget Understand reasons for variation Take remedial measures if required Plan again based on actual performance and feedback www.bizkul.com
22
Budgets
Keep company objectives in mind Long term and short term Rolling budgets
www.bizkul.com
23
Budgets
Master budget, comprising of detailed budgets for eg. budgets for – Income – Production – Direct costs – R&D – Administration www.bizkul.com
24
Product budget
Expected sale Inventory on hand Production schedule Direct costs Indirect costs Company policies and strategy www.bizkul.com
25
Life cycle costing
Considers entire life cycle of product from start to finish Provides important information for pricing decisions For example, if a mobile phone is built, if the R&D costs are high for the company, the repairs and maintenance cost to the customer may be low; so the life cycle is across the life of the product and considers costs www.bizkul.com and impact on prices 26
Life cycle costs
Upstream costs – R&D, design, prototyping, testing, quality development
Manufacturing/Operations costs – Purchasing, manufacture/service
Downstream costs – marketing, sales and distribution, customer service and warranty www.bizkul.com
27
Life cycle costs
Product life cycle costs vary with industry and nature of industry R&D is not only at start of product life, this may also occur at other stages, ie development of additional features in product Life cycle may also depend on markets targeted, ie country, region, socio-economic background etc. www.bizkul.com 28
Implementation of LCC
Identify stages in product life cycle Identify target customer Understand target customers perspective and estimate need Analyse cost and pricing in detail Educate employees about LCC www.bizkul.com
29
Implementation of LCC
Develop product and pricing structure based on LCC Create appropriate organisation structure for implementation Educate customer on LCC, eg. mobile phone referred to in earlier slide Focus on strategic marketing to address customer requirements and needs, stated and unstated Continuous life cycle budgeting and monitoring and modify/change as required www.bizkul.com 30
Life cycle costing benefits
Optimisation of profit over product life Full set of costs associated with products are ascertained – Most accounting systems capture manufacturing costs – Other areas like R&D at start and customer service as close do not get much importance www.bizkul.com
31
Life cycle costing benefits
Differences in percentages in committed costs at initial stage of business is highlighted – The higher the initial costs, the more critical it is for management to develop better predictions about revenues
www.bizkul.com
32
Life cycle costing benefits
Interrelationships across cost categories are highlighted – Many companies with high R&D & product refinement costs may experience less customer service costs and vice versa. Such costs are often hidden and affect quality of product
www.bizkul.com
33
Pricing
Intuitive Rule of thumb Trial and error Discount Premium Mark up www.bizkul.com
34
Pricing decisions Influenced by Costs Competitors Customers Time horizon – short run or long run decisions Strategic reasons www.bizkul.com
35
Target Pricing
Develop product Set target price Try to achieve target cost Target cost = Competitive price – desired profit www.bizkul.com
36
Pricing for short run
Decide on relevant costs that should be used Compute costs, direct, indirect and total Compute any special costs that need to be incurred and savings that may be possible Decide on pricing based on other factors such as long term impact, competition etc. www.bizkul.com
37
Pricing for long run
Important to consider long term pricing for long term sustainability and growth of business Initial pricing and short term pricing should keep long term pricing in mind Image and brand of business to be considered in pricing Costs to be understood and allocated Consistency in pricing in long term www.bizkul.com
38
…..to trigger thinking
www.bizkul.com
39
A cup of coffee
A cup of coffee costs Rs. 10 to make
HOW will you plan to price this?
……….. continued.. www.bizkul.com
40
A cup of coffee
Will you charge based on the price of coffee in similar coffee shops and restaurants?
……….. continued.. www.bizkul.com
41
A cup of coffee
Will you charge cost plus a margin?
……….. continued..
www.bizkul.com
42
A cup of coffee
OR will you think differently?
……….. continued..
www.bizkul.com
43
A cup of coffee For example …
You could charge differently during the rush hour You could have special rates in non rush hours
www.bizkul.com
44
Some thoughts… You can … if you want
Think differently about your pricing Think differently about your negotiations for pricing and selling www.bizkul.com
45
Related Documents
Life Cycle Costing
May 2020 15
Life Cycle Costing
November 2019 24
Life Cycle Costing
December 2019 8
Costing
December 2019 40
