Form 3 Chapter 8
This document was uploaded by user and they confirmed that they have the permission to share it. If you are author or own the copyright of this book, please report to us by using this DMCA report form. Report DMCA
Overview
Download & View Form 3 Chapter 8 as PDF for free.
More details
- Words: 570
- Pages: 8
CHAPTER 8 GENERATION OF ELECTRICITY
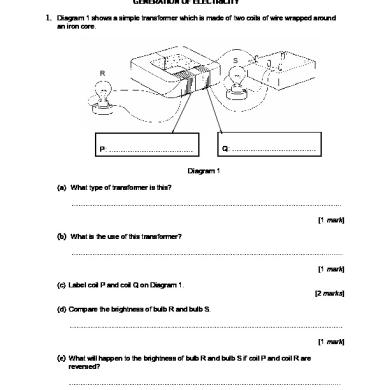
1. Diagram 1 shows a simple transformer which is made of two coils of wire wrapped around an iron core.
S R
P: ………………………………
Q: ………………………………
Diagram 1 (a) What type of transformer is this? …………………………………………………………………………………………………….. [1 mark]
(b) What is the use of this transformer? ……………………………………………………………………………………………….......... [1 mark] (c) Label coil P and coil Q on Diagram 1. [2 marks] (d) Compare the brightness of bulb R and bulb S. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… [1 mark]
(e) What will happen to the brightness of bulb R and bulb S if coil P and coil R are reversed? ………………………………………………………………………………………………..........
191
[1 mark] 2. Diagram 2 shows the structure of a 3-pin plug Q: ………………………..
S P: ……………………….. R: ………………………..
Diagram 2
(a) On Diagram 2, label structure P, Q and R using the following words. Live wire
Earth wire
Neutral wire [3 marks]
(b) Draw line to show the correct match between the wires and their functions Wire
Function
P
Carry electric current back to the mains
Q
Carry leaked current to the Earth
R
Carry electric current to the electrical appliance [3 marks]
192
(c) Draw line to show the correct match between the wires and their colours. Wire
Colour Blue
P
Q
Brown
R
Yellow with green stripes [3 marks]
(d) (i) Name the component labelled S. …………………………………………………………………………………………………… [1 mark] (ii) State the function of the component labelled S ………………………………………………………………………………………………….. [1 mark]
193
3. Diagram 3 shows two commercial methods of generating electricity commonly used in Malaysia. P
Q
Diagram 3 (a) Name the type of electric generator shown in Diagram 3. P :.....……………………………………………………………………………………………….. Q: ……….………………………………………………………………………………………….. [2 marks]
(b) State the energy change that takes place in Q. …………………………………………………………………………………………………….. [1 mark]
(c) State one disadvantage of using P to generate electricity. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… [1 mark] (d) State one advantage of using Q to generate electricity. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… [1 mark] (e) Apart from P and Q, name another type of electrical generator used in Malaysia. ………………………………………………………………………………………………………
194
[1 mark]
4. Diagram 4.1 shows the electrical wiring system in the house. Q: ……………………………..
P: …………………………
R: ……………………… Diagram 4.1
(a) On Diagram 4.1, label P, Q and R with the following words. Fuse box
Main fuse
Electric meter [3 marks]
(b) What is the function of (i)
P? ………………………………………………………………………………………… ……
(ii)
Q? ………………………………………………………………………………………… ….. [2 marks]
(c) Why are the lights in the lighting circuit connected in parallel? ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… [1 mark]
195
(d) Diagram 4.2 shows the readings of an electric meter for a household. Previous Reading
0
2
4
6
5
Current Reading
5
0
2
4
9
kWh
3
8 kWh
DIAGRAM 4.2 (i)
Calculate the number of electrical energy units used by the household.
[2 marks] (ii)
Table 4.3 shows the rate of electrical energy charged by the electrical power supplier. Charge First Consecutive
Unit 200 500
Rate RM 0.32 RM 0.38
Table 4.3 Calculate the cost of electrical energy used by the household in (d)(i).
196
[2 marks] 5. Diagram 5 shows the electrical energy transmission and distribution system.
P: ……………………………..
Q: ……………………………..
M
N
R: ……………………………
Diagram 5 (a) Label P, Q and R on Diagram 5 using the following words. Switch zone
Power station
Main substation [3 marks]
(b) What is the function of Q? ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… [1 mark] (c) What is the difference between M and N? ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… [1 mark]
197
(d) State one advantage of the National Grid Network. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… [1 mark]
198
1. Diagram 1 shows a simple transformer which is made of two coils of wire wrapped around an iron core.
S R
P: ………………………………
Q: ………………………………
Diagram 1 (a) What type of transformer is this? …………………………………………………………………………………………………….. [1 mark]
(b) What is the use of this transformer? ……………………………………………………………………………………………….......... [1 mark] (c) Label coil P and coil Q on Diagram 1. [2 marks] (d) Compare the brightness of bulb R and bulb S. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… [1 mark]
(e) What will happen to the brightness of bulb R and bulb S if coil P and coil R are reversed? ………………………………………………………………………………………………..........
191
[1 mark] 2. Diagram 2 shows the structure of a 3-pin plug Q: ………………………..
S P: ……………………….. R: ………………………..
Diagram 2
(a) On Diagram 2, label structure P, Q and R using the following words. Live wire
Earth wire
Neutral wire [3 marks]
(b) Draw line to show the correct match between the wires and their functions Wire
Function
P
Carry electric current back to the mains
Q
Carry leaked current to the Earth
R
Carry electric current to the electrical appliance [3 marks]
192
(c) Draw line to show the correct match between the wires and their colours. Wire
Colour Blue
P
Q
Brown
R
Yellow with green stripes [3 marks]
(d) (i) Name the component labelled S. …………………………………………………………………………………………………… [1 mark] (ii) State the function of the component labelled S ………………………………………………………………………………………………….. [1 mark]
193
3. Diagram 3 shows two commercial methods of generating electricity commonly used in Malaysia. P
Q
Diagram 3 (a) Name the type of electric generator shown in Diagram 3. P :.....……………………………………………………………………………………………….. Q: ……….………………………………………………………………………………………….. [2 marks]
(b) State the energy change that takes place in Q. …………………………………………………………………………………………………….. [1 mark]
(c) State one disadvantage of using P to generate electricity. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… [1 mark] (d) State one advantage of using Q to generate electricity. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… [1 mark] (e) Apart from P and Q, name another type of electrical generator used in Malaysia. ………………………………………………………………………………………………………
194
[1 mark]
4. Diagram 4.1 shows the electrical wiring system in the house. Q: ……………………………..
P: …………………………
R: ……………………… Diagram 4.1
(a) On Diagram 4.1, label P, Q and R with the following words. Fuse box
Main fuse
Electric meter [3 marks]
(b) What is the function of (i)
P? ………………………………………………………………………………………… ……
(ii)
Q? ………………………………………………………………………………………… ….. [2 marks]
(c) Why are the lights in the lighting circuit connected in parallel? ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… [1 mark]
195
(d) Diagram 4.2 shows the readings of an electric meter for a household. Previous Reading
0
2
4
6
5
Current Reading
5
0
2
4
9
kWh
3
8 kWh
DIAGRAM 4.2 (i)
Calculate the number of electrical energy units used by the household.
[2 marks] (ii)
Table 4.3 shows the rate of electrical energy charged by the electrical power supplier. Charge First Consecutive
Unit 200 500
Rate RM 0.32 RM 0.38
Table 4.3 Calculate the cost of electrical energy used by the household in (d)(i).
196
[2 marks] 5. Diagram 5 shows the electrical energy transmission and distribution system.
P: ……………………………..
Q: ……………………………..
M
N
R: ……………………………
Diagram 5 (a) Label P, Q and R on Diagram 5 using the following words. Switch zone
Power station
Main substation [3 marks]
(b) What is the function of Q? ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… [1 mark] (c) What is the difference between M and N? ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… [1 mark]
197
(d) State one advantage of the National Grid Network. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… [1 mark]
198
Related Documents
Form 3 Chapter 8
May 2020 7
Form 3 Chapter 3
May 2020 15
Form 2 Chapter 8
May 2020 19
Form 3 Chapter 10
May 2020 8
Form 3 Chapter 7
May 2020 14