2123.docx
This document was uploaded by user and they confirmed that they have the permission to share it. If you are author or own the copyright of this book, please report to us by using this DMCA report form. Report DMCA
Overview
Download & View 2123.docx as PDF for free.
More details
- Words: 503
- Pages: 5
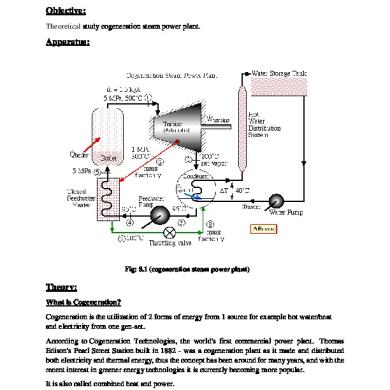
Experiment # 3 Objectives: To perform Compression test on UTM and to Determine Mechanical/Material Properties of the Sample in Compression.
Apparatus (Equipment): Universal Testing Machine Extensometer (with dial indicator) Scale
Fig 3.1 (UTM)
Theory: Universal Testing Machine (UTM): A Universal Testing Machine (UTM) is used to test both the tensile and compressive strength of materials. Universal Testing Machines are named as such because they can perform many different varieties of tests on an equally diverse range of materials, components, and structures. Most UTM models are modular, and can be adapted to fit the customer’s needs.
Universal Testing Machines can accommodate many kinds of materials, ranging from hard samples, such as metals and concrete, to flexible samples, such as rubber and textiles. This diversity makes the Universal Testing Machine equally applicable to virtually any manufacturing industry. The UTM is a versatile and valuable piece of testing equipment that can evaluate materials properties such as tensile strength, elasticity, compression, yield strength, elastic and plastic deformation, bend compression, and strain hardening. Different models of Universal Testing Machines have different load capacities, some as low as 5kN and others as high as 2,000kN. Tests can also be performed in controlled environmental conditions. This is achieved by placing the Universal Testing Machine into an environmental room or chamber. For example, metals testing can be conducted at extreme temperatures: from -196°C (-321°F) to over 1000°C (1800°F).
Strain Rate: Strain rate is the change in strain (deformation) of a material with respect to time. The strain rate at some point within the material measures the rate at which the distances of adjacent parcels of the material change with time in the neighborhood of that point.
Preload: A test segment where the crosshead moves to load the specimen to a specified value before a test starts. Data is not captured during the preload segment.
Procedure: Dimension of test piece is measured at three different places along its height/length to determine the average cross-section area. Ends of the specimen should be plane. For that the ends are tested on a bearing plate. The specimen is placed centrally between the two compressions plates, such that the center of moving head is vertically above the center of specimen. Load is applied on the specimen by moving the movable head. The load and corresponding contraction are measured at different intervals. The load interval may be as 500 kg. Load is applied until the specimen fails.
Calculation:
Sr#
Force
Area
Stress
(N)
(m2)
(N/m2)
Graph:
Fig 3.2 (Time-Defore Curve)
Fig 3.3(Load-Defore Curve)
Fig 3.4(Load-Time Curve)
Precautions: The specimen must be kept at the Centre of cross-head so that a uniform compressive loading can be assured on the specimen. The loading is to be increased gradually. The size of the specimen is to be measured accurately.
Comments: In this experiment we can perform Compression test on UTM. In This experiment we can Decrease length of the material. After decrease length material is break.
Apparatus (Equipment): Universal Testing Machine Extensometer (with dial indicator) Scale
Fig 3.1 (UTM)
Theory: Universal Testing Machine (UTM): A Universal Testing Machine (UTM) is used to test both the tensile and compressive strength of materials. Universal Testing Machines are named as such because they can perform many different varieties of tests on an equally diverse range of materials, components, and structures. Most UTM models are modular, and can be adapted to fit the customer’s needs.
Universal Testing Machines can accommodate many kinds of materials, ranging from hard samples, such as metals and concrete, to flexible samples, such as rubber and textiles. This diversity makes the Universal Testing Machine equally applicable to virtually any manufacturing industry. The UTM is a versatile and valuable piece of testing equipment that can evaluate materials properties such as tensile strength, elasticity, compression, yield strength, elastic and plastic deformation, bend compression, and strain hardening. Different models of Universal Testing Machines have different load capacities, some as low as 5kN and others as high as 2,000kN. Tests can also be performed in controlled environmental conditions. This is achieved by placing the Universal Testing Machine into an environmental room or chamber. For example, metals testing can be conducted at extreme temperatures: from -196°C (-321°F) to over 1000°C (1800°F).
Strain Rate: Strain rate is the change in strain (deformation) of a material with respect to time. The strain rate at some point within the material measures the rate at which the distances of adjacent parcels of the material change with time in the neighborhood of that point.
Preload: A test segment where the crosshead moves to load the specimen to a specified value before a test starts. Data is not captured during the preload segment.
Procedure: Dimension of test piece is measured at three different places along its height/length to determine the average cross-section area. Ends of the specimen should be plane. For that the ends are tested on a bearing plate. The specimen is placed centrally between the two compressions plates, such that the center of moving head is vertically above the center of specimen. Load is applied on the specimen by moving the movable head. The load and corresponding contraction are measured at different intervals. The load interval may be as 500 kg. Load is applied until the specimen fails.
Calculation:
Sr#
Force
Area
Stress
(N)
(m2)
(N/m2)
Graph:
Fig 3.2 (Time-Defore Curve)
Fig 3.3(Load-Defore Curve)
Fig 3.4(Load-Time Curve)
Precautions: The specimen must be kept at the Centre of cross-head so that a uniform compressive loading can be assured on the specimen. The loading is to be increased gradually. The size of the specimen is to be measured accurately.
Comments: In this experiment we can perform Compression test on UTM. In This experiment we can Decrease length of the material. After decrease length material is break.
More Documents from "Akram"
Experiment8.pdf
December 2019 26
2123.docx
December 2019 33
List Of Experiments Mom 1.docx
December 2019 13
Experiment5.docx
December 2019 13
